Role of Letter of Credit in Business: In the modern era of trade, letter of credit is playing significant role in Business financing, earlier letter of credit was only used as international financing device in International trade, however now a days it is quite popular in domestic trade also. Theories said that Letter of credit is not a new term in this world. Some believes that origins of letters of credit go back to ancient Egypt and Babylon.
It can be say that ‘Necessity is mother of Invention’, when business realized mutual lack of trust between parties and observed that business cannot be made simply by handshake, some surety to seller is required that buyer will not make default in payment after receiving the goods or services, then Letter of credit come in picture and slowly becomes necessity of business. Originally it was a letter addressed by the buyer’s bank to the seller’s bank stating they would guarantee payment the seller in case of the buyer’s default.
Quick Links
Role of Letter of Credit in Business
L/Cs plays an important role in the trade of a country, especially in its international trade. In most of the cases, the exporters (sellers) are personally not acquainted with the importers (buyers) in foreign countries. In such cases the exporters bear great risk, if they draw bills on importers, after having dispatched the goods as per their orders, because if the latter default in accepting the bills or making the payment, the exporter will suffer with heavy losses. To avoid such kind of risks, the exporters ask the importers to arrange a letter of credit from their banker in favour of themselves, on the basis of which goods may be exported to the foreign importers
Meaning of letter of Credit
Letter of Credit (‘L/C’), also known as a documentary credit is a payment mechanism used specially in international trade. In an L/C, buyer’s bank undertakes to make payment to seller on production of documents stipulated in the document of L/C.
According to Uniform Custom and Practice for Documentary Credit(UCP), 600,Letter of Credit means ‘any arrangement, however named or described,thatis irrevocable and thereby constitutes a definite undertaking of the issuing bank to honour a complying presentation’.
Uniform Custom and Practice for Documentary Credit (UCP), 600 provides standard format of Letter of credit and Uniform Customs and Practices for Documentary Credits – 600 (UCPDC-600) apply to any LC when its text expressly indicates that it is subject to these rules. The rules are binding to all parties unless expressly modified or excluded.
Parties of Letter of credit
There are mainly four parties in letter of Credit which is as under;
| Applicant | Applicant is the buyer or importer of goods or services. The Bank opens the L/C on behalf of buyer. He is termed as Applicant or Opener of Letter of Credit. |
| Issuing Bank | Issuing bank is a bank which opens L/C and undertakes to make payment to the beneficiary (seller/ exporter) on submission of relevant document( Delivery challan, GST Invoice, shipping documents, transport slip as the case may be) as per the terms and condition of L/C. |
| Beneficiary | Beneficiary is the seller / exporter of goods in whose favour L/C is opened. |
| Advising Bank | Advising Bank is the seller bank through whom LC is advised to the beneficiary. |
| Confirming Bank | Confirming Bank is the bank which in addition to L/C issuing bank, undertakes the responsibility of payment under L/C. This is required since the L/C issuing bank may not be known to the exporter and he therefore needs reputed bank from his country to add confirmation to the LC. Confirming Bank may or may not be there. |
How the Letter of credit work
The process of letter of credit can be understood through following diagram:
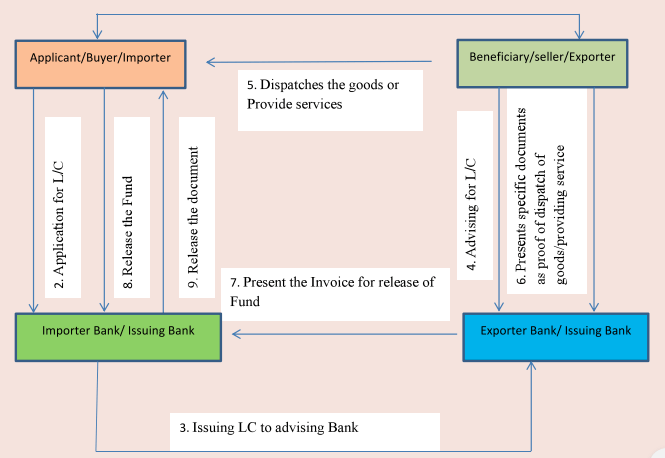
- 1) There is sale/supply contract between Buyer (Applicant) and seller (Beneficiary) and supply contract is having clause that buyer can make the payment through L/C and name of advising bank is given in supply contract.
- 2) Buyer (Applicant) approach to their Bank for issuing the Letter of credit with the name of buyer Bank (Advising Bank). Usually there is standard format of letter of credit, however there may be some specific clause mutually decided by both the parties and agreed by their bankers.
- 3) Issuing Bank issue letter of credit to advising bank as mentioned in supply contract.
- 4) Seller (Beneficiary) approach to their Bank (Advising Bank) for letter of credit.
- 5) Seller (Beneficiary) dispatches the goods/provides the service as per the supply contract to buyer.
- 6) Seller (Beneficiary) present the specified documents to Advising bank as proof of dispatch of goods. The specified documents may include the following;
- a) Financial Documents: Bill of Exchange, Co-accepted Draft
- b) Commercial Documents : Delivery Challan or GST Invoice or Debit Note or Commercial Invoice
- c) Shipping Documents: Lorry Receipt or E-way Bill or Railway receipt
- d) Any other documents as prescribed in sale contract
- 7) Advising Bank present the documents to issuing bank for releasing of fund and after receiving the fund for issuing bank provide fund to beneficiary.
- 8) Issuing Bank release documents to Applicant after receiving the fund
There may be time lag for releasing the fund for issuing bank to advising bank and receiving the fund from Applicant. Bank charge fixed fee for the letter of credit as compensation of time lag. Usually bank charge fee from buyer /applicant of L/C.
Types of Letter of credit
The following are the types of Letter of Credit
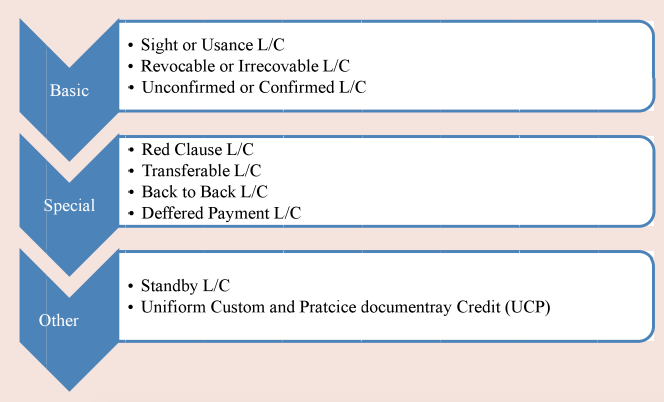
A) Basic Type of Letter of Credit
i) Sight or Usance Letter of Credit
When an issuing bank makes payment to the beneficiary immediately on receipt and verification of the documents from the beneficiary (Seller/ exporter); it is called a sight letter of credit. On the contrary where the issuing bank agrees to pay the beneficiary only on the expiry of the letter of credit, the L/C issued is called usance letters of credit.
Usance letters of credit is considered risky from the point of view of an exporter/seller as he is left unpaid for a considerable period of time after the delivery of the goods or providing of service.
ii) Revocable or Irrevocable L/C
Revocable letter of credit can be cancelled anytime by the Issuing bank without the consent of or without intimating the beneficiary. Irrevocable letter of credit cannot be cancelled or withdrawn by the issuing bank without informing and receiving an approval from the beneficiary. Revocable letter is very risky from the seller/beneficiary point of view.
iii) Unconfirmed or Confirmed L/C
Confirmed L/C wherein apart from issuing bank, Seller acquire the guarantee of payment from confirming Bank. Unconfirmed L/C that is assured only by the issuing Bank and does not require the guarantee from second bank.
B) Special Type of Letter of Credit
i) Red Clause L/C
A letter of credit that partially pays the beneficiary before the goods are shipped or the services are performed. The advance is paid against the written confirmation from the seller.
ii) Transferable L/C
A Transferable Credit is one in which a beneficiary can transfer his rights to third parties. In trading business,this kind of L/c is used, wherein beneficiary (Trader of goods) transferred the letter of credit to next chain of supplier or manufacture. The beneficiary work as intermediary of actual supplier or manufacture.
iii) Back to Back L/C
In Back to Back Letter of credit, seller of goods requested to bank to issue letter of credit in favour of their input supplier. Seller of goods acts beneficiary as well as applicant.
iv) Deferred Payment L/C
Deferred Letter of Credit is a type of Letter of Credit in which a conditional undertaking is taken by the bank to pay the seller on behalf of the buyer on a specified future date after completion of the transaction. It is looking similar to usance letter of credit; however, in usance Letter of Credit, the bank makes the payment to the beneficiary on a pre-determined date after submission of necessary documents. In deferred letter of credit, specified future date after completion of the transaction .
C) Other type of Letter of Credit
i) Standby Letter of Credit
Stand by Letter of credit, that assure that in case of buyer failure to make the payment, Bank will pay to seller
ii) Uniform Custom and Practice documentary Credit (UCP)
Uniform Customs and Practice (UCP) for Documentary Credits is a publication of International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) which is a voluntary code applied by the banks all over the world. As per UPC Letter of credit can only be irrevocable credit.
What is the Common discrepancy in Letter of Credit?
In the following circumstances bank may raise discrepancy and stop releasing the payment until discrepancy is not removed;
- i) Inconsistency in Documents; As per the terms and condition of L/c; relevant documents for claim will be Invoice, however seller present the Debit note for payment. The banker may raise discrepancy. While framing the terms and condition of L/C; Seller should ensure that all the relevant documents (Like Delivery challan, Debit Note, invoice, commercial invoice) used in commercial business parlance is included in Letter of credit to avoid dispute
- ii) Incorrect data; documents presents is not comply with the terms and condition of Letter of credit.
- iii) Late shipment ; Goods shipped after the expiry of date as mentioned in terms and condition of letter of credit
- iv) Late Presentation: In terms and condition of letter of credit, it is stated that seller will present the documents within 24 hours of dispatch of goods, however documents is presented before bank after the expiry of 24 hours.
- v) Letter of credit expired: Documents presented after the expiry of letter of credit cover period.
- vi) Absence of documents : Complete Documents mentioned in terms and condition of Letter of creditis not submitted to bank
- vii) Incorrect description of goods : In terms and condition of Letter of credit, goods is mentioned as X, however seller charge some other charges like incentive for fulfillment for timely fulfillment of contract and the same is not included in L/C terms and condition, in that case bank may raise objection.
Recommended







